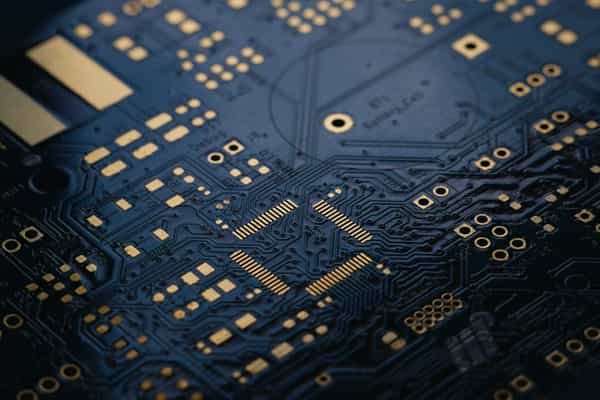
High Tg PCB Manufacturing for High Temperature Applications
We manufacture reliable High Tg PCBs using Tg 170–180+ FR‑4 materials, engineered for automotive, power electronics, industrial control, and telecom applications that must survive elevated temperatures and demanding duty cycles.
- High Tg 170–180+ FR‑4 materials, lead‑free compatible for multiple reflow cycles.
- Multilayer and HDI capabilities with controlled CTE and low warpage for high‑reliability designs.
- Optimized processes for high temperature PCBs: lamination, drilling, desmear, and thermal stress testing.
- Fast engineering review and quotations for prototypes and small to medium volume production.
Upload your Gerber files and requirements to receive a High Tg PCB quotation and material recommendation within 24 hours.
Request a High Tg PCB Quote
Share your design files and operating conditions. Our engineers will review your requirements and suggest suitable High Tg materials and stack‑ups.
What Is a High Tg PCB?
A High Tg PCB is a printed circuit board made with materials that have a higher glass transition temperature (Tg), so the board stays mechanically stable and reliable at elevated temperatures.
Tg is the temperature at which the PCB substrate changes from a hard, glassy state to a softer, rubber‑like state. When the operating or assembly temperature approaches this point, standard FR‑4 begins to warp, expand, or lose long‑term reliability.
Standard FR‑4 materials typically have a Tg of about 130–140 ℃, while High Tg FR‑4 materials are engineered with Tg values of 170 ℃ or higher, and some ultra‑high Tg laminates even exceed 180 ℃.
By using these High Tg materials, High Tg PCBs offer better thermal stability, dimensional control, and resistance to thermal cycling than conventional FR‑4 boards in demanding environments.
Why High Tg Matters for Your PCB
High Tg PCBs are not only about surviving high temperatures; they also keep your board flat, reliable, and electrically stable over the product’s lifetime.
- Improved thermal stability: High Tg materials withstand higher operating and lead‑free reflow temperatures without excessive softening or deformation.
- Better mechanical reliability: Reduced board warpage, lower risk of delamination, and stronger plated through‑hole reliability under thermal cycling.
- More consistent electrical performance: Stable dielectric and impedance behavior at elevated temperatures helps maintain signal integrity in dense or high‑reliability designs.
- Ideal for heat‑intensive and multilayer designs: High power density, multilayer and HDI boards, automotive, aerospace, industrial control, power inverters, and telecom equipment often require High Tg PCBs for long‑term reliability.
When Do You Need a High Tg PCB?
In many projects, a standard FR‑4 material is sufficient, but you should consider a High Tg PCB when your design is exposed to higher temperatures, power densities, or more demanding assembly conditions.
- The maximum operating temperature of your PCB is in the 130 ℃ range or higher, or close to the material’s Tg rating, leaving less than about 25 ℃ of safety margin.
- Your design uses high‑power components or has high power density, so internal heat generation can overload heatsinks and traditional FR‑4 boards.
- The PCB is multilayer or HDI, with many layers, buried/blind vias, or thick copper, where lamination, drilling, and lead‑free soldering expose the board to repeated high thermal stress.
- The assembly requires lead‑free reflow profiles with higher peak temperatures, or your product must endure frequent temperature cycling over a long lifetime.
- The device operates in harsh environments such as near engines, power equipment, outdoor enclosures, or industrial lines with high vibration, humidity, or chemicals, where extra thermal and mechanical robustness is essential.
In these situations, choosing a High Tg PCB improves safety margins, reduces the risk of warpage and delamination, and helps keep your electronics reliable over the full service life of the product.
High Tg PCB Materials and Typical Tg Values
High Tg PCBs rely on specialized FR‑4 laminates that can maintain mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and electrical performance at elevated temperatures and during lead‑free assembly. While standard FR‑4 usually has a Tg around 130–140 ℃, High Tg FR‑4 materials are formulated with Tg values of 170 ℃ and above for more demanding applications.
| Material (example) | Tg (℃) (typical) | Td (℃, approx.) | Typical z‑axis CTE (50–260 ℃) | Layers range | Typical applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Tg FR‑4 Tg170 class | 170+ | 330–340 | Lower expansion than standard FR‑4 | 4–12 | General high‑temperature boards, industrial control, LED lighting, lead‑free assembly. |
| ITEQ IT‑180A (High Tg FR‑4) | ≈180 | ≈340–350 | Around 3.0% z‑axis expansion, good thermal stability | 6–20 | Multilayer and HDI boards in automotive, telecom, power, and industrial electronics. |
| TUC TU‑768 (High Tg FR‑4) | 170–190 | ≈340–350 | Around 2.5–3.0% z‑axis expansion, good CAF resistance | 8–24 | High‑layer‑count, high‑speed digital, servers, base stations, automotive electronics. |
| Ultra‑high Tg FR‑4 / hybrid systems | 180–250 | 340+ | Very low CTE and high thermal endurance | 8–30 | Harsh‑environment, aerospace, defense, and high‑reliability power or RF applications. |
Selecting the right High Tg material depends on your maximum operating temperature, layer count, copper thickness, and reliability targets. If you share your stack‑up, thermal requirements, and performance goals, our engineers can recommend suitable High Tg laminates and complete material sets for your design.
Our High Tg PCB Manufacturing Capabilities
We combine High Tg materials with controlled processes to fabricate reliable multilayer and HDI PCBs for demanding applications. The following capabilities give an overview of the High Tg PCB technologies we can support for prototypes and volume production.
- Board types: High Tg FR‑4 multilayer, HDI, and mixed‑dielectric constructions.
- Layer count: 2–20 layers for standard High Tg FR‑4 builds, with options for higher layer counts on request.
- Max board size: Up to 510 mm × 610 mm (20″ × 24″) panel capability for most High Tg stack‑ups.
- Finished board thickness: From 0.6 mm to 3.2 mm, depending on stack‑up, copper weight, and layer count.
- Copper thickness: 1–3 oz outer layers and 0.5–3 oz inner layers for High Tg power, industrial, and automotive applications.
- Minimum trace / space: Down to 4/4 mil (0.10/0.10 mm) for standard High Tg designs, with finer features available for selected stack‑ups.
- Surface finishes: ENIG, immersion tin, immersion silver, OSP, lead‑free HASL, hard gold, and other finishes compatible with High Tg laminates.
- Testing and inspection: 100% electrical test, AOI, impedance control, and reliability testing tailored to High Tg and lead‑free requirements.
If your design requires specific High Tg materials, unusual stack‑ups, or tighter design rules than those listed here, our engineering team can review your files and confirm manufacturability before production. Send us your Gerber files, stack‑up, and key reliability requirements to receive a detailed DFM check and High Tg PCB quotation.
Design Guidelines: How to Choose Tg and Design for High Temperature
Choosing the right Tg and designing correctly for high temperature operation is critical to avoid warpage, delamination, and reliability issues in the field. The points below provide practical rules of thumb you can use during material selection and PCB layout for High Tg designs.
Matching Tg to Your Operating and Assembly Temperatures
When selecting a High Tg material, you should always look at both the maximum operating temperature of the board and the peak assembly temperatures.
- Keep a safety margin of roughly 20–30 ℃ between your maximum continuous operating temperature and the material’s Tg rating. For example, a design running around 140 ℃ should normally use a material with Tg ≥170 ℃.
- Consider both ambient and self‑heating from power devices, since local hot spots can push parts of the board much closer to Tg than the average board temperature.
- For lead‑free assembly with multiple reflow cycles, High Tg materials are strongly recommended even if the steady‑state operating temperature is moderate, because the board still sees high peak temperatures during soldering.
- In products that must survive repeated thermal cycling or harsh qualification tests, choose a material with a higher Tg and good Td (decomposition temperature) rather than only matching the minimum requirement.
Layout and Stack‑Up Tips for High Tg PCBs
High Tg materials give you more thermal margin, but good stack‑up and layout practices are still essential for reliability.
- Balance copper and layer thickness in the stack‑up to minimize warpage, especially for High Tg multilayer and HDI boards.
- Use adequate annular rings, via aspect ratios, and drill sizes to improve plated through‑hole reliability under thermal expansion and contraction.
- Provide generous copper areas and thermal vias under high‑power components so that heat spreads into the High Tg substrate instead of concentrating in small hot spots.
- For high‑speed or RF sections, consider both Tg and dielectric properties such as Dk and Df to maintain signal integrity across the full temperature range.
If you are not sure which Tg level, material grade, or stack‑up is best for your design, you can send us your Gerber files, target operating temperature, and reliability requirements. Our engineers will review your design and recommend suitable High Tg materials, stack‑ups, and potential layout optimizations before production.
Industries and Applications for High Tg PCBs
High Tg PCBs are widely used wherever electronics must handle elevated temperatures, high power densities, or long‑term reliability in harsh environments. The examples below highlight typical industries and applications where High Tg materials provide clear advantages over standard FR‑4.

Power Electronics & Industrial Control
Automotive & Transportation

Telecom, Networking & Data Centers

Aerospace, Defense & Harsh Environment Electronics
Whether your project is in power electronics, automotive, telecom, or aerospace, we can match High Tg PCB materials and stack‑ups to the specific thermal and reliability requirements of your industry.
Frequently Asked Questions About High Tg PCBs
A High Tg PCB is a board made with materials whose glass transition temperature is significantly higher than standard FR‑4, so the laminate stays stable at elevated temperatures. While ordinary FR‑4 typically has a Tg around 130–140 ℃, High Tg materials usually start at about 170 ℃ and can go to 180 ℃ or higher.
You should consider a High Tg PCB when your maximum continuous operating temperature is close to or above the Tg of standard FR‑4, leaving less than about 20–30 ℃ of safety margin. High Tg is also recommended for high‑power and high‑density designs, multilayer and HDI boards, harsh automotive or industrial environments, and products that must pass demanding thermal cycling or reliability tests.
A higher Tg gives more thermal margin and often better mechanical stability, but it also tends to increase material cost and may not be necessary for low‑temperature applications. The best choice is to match Tg to your operating and assembly temperatures, reliability targets, and budget instead of simply choosing the highest available Tg.
High Tg materials are strongly preferred for lead‑free reflow because the peak soldering temperatures are higher and boards may see multiple thermal cycles during assembly. In many lead‑free designs, using High Tg FR‑4 significantly reduces the risk of warpage, delamination, and plated through‑hole damage compared with standard Tg laminates.
To prepare an accurate High Tg PCB quotation, we typically need your Gerber or design files, layer count, board size, finished thickness, copper weight, minimum trace/space, surface finish, and expected quantities. It is also very helpful if you can share your maximum operating temperature, preferred Tg level (if known), and any special reliability or industry standards the board must meet.
Yes. If you are unsure which Tg or laminate family is best, you can send us your stack‑up, operating conditions, and reliability requirements. Our engineers will review your design and recommend suitable High Tg materials, stack‑ups, and any design adjustments needed to improve manufacturability and long‑term reliability.
Ready to Discuss Your
High Tg PCB Project?
High Tg PCBs can significantly improve the reliability of electronics that must operate at elevated temperatures, under high power density, or in harsh environments. If you share your design files and key requirements, our engineering team can help you select suitable High Tg materials and stack‑ups and provide a detailed quotation.
Upload your Gerber files and tell us about your operating conditions to receive a High Tg PCB quotation and material recommendation.
- Engineering review focused on High Tg material selection, stack‑up, and manufacturability.
- Support for prototypes, small and medium production with flexible lead times.
- Experience in automotive, power electronics, industrial control, telecom, and other demanding industries.