Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics, connecting components to create functional devices. Rigid PCBs and flex PCBs serve similar purposes but differ significantly in materials, design, and applications. This article explores the key differences between rigid PCB and flex PCB, including their advantages, use cases, and how to choose the right one for your project. Whether you’re designing consumer electronics or compact wearables, JHYPCB offers expert solutions.

Key Differences Between Rigid PCB and Flex PCB

Rigid PCBs and flex PCBs offer distinct advantages in electronics design, differing in flexibility, cost, and applications. The table below highlights the differences between rigid PCB and flex PCB, followed by detailed explanations:
Feature | Rigid PCB | Flex PCB |
|---|---|---|
Flexibility | Inflexible, fixed structure | Bendable, twistable for complex shapes |
Cost | Lower cost, ideal for high-volume | Higher cost due to specialized materials |
Applications | Consumer electronics, industrial | Wearables, automotive, aerospace |
Durability | Strong but less vibration-resistant | High resistance to vibration/shock |
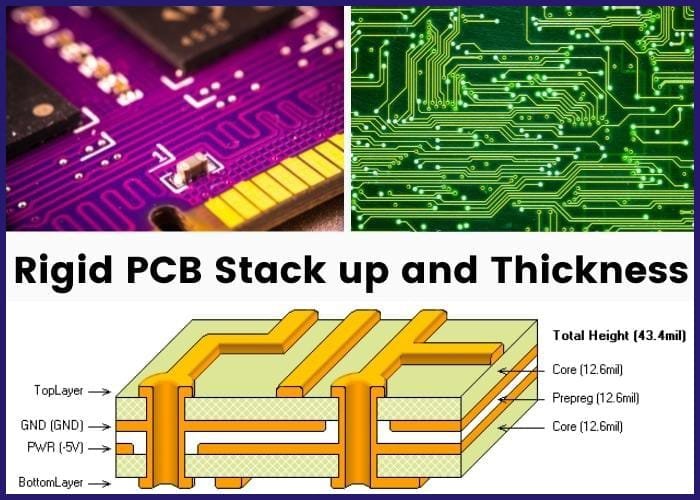
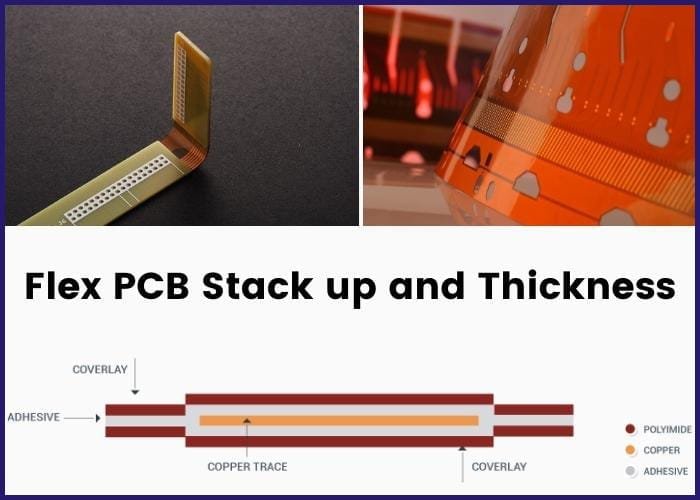
Manufacturing | Uses FR4 and solder mask | Uses polyimide and coverlay |
Detailed Differences
- Flexibility: Flex PCBs can bend and fold, making them ideal for compact devices like smartwatches and foldable phones. Rigid PCBs suit space-abundant devices like desktops. Learn more about flex PCB design tips.
- Connectivity: Flex PCBs enable reliable connections in dynamic applications, such as laptop display connectors.
- Weight: Flex PCBs are lightweight, perfect for drones and unmanned vehicles.
- Durability: Flex PCBs absorb vibrations better, widely used in medical devices and aerospace.
- Heat Resistance: Flex PCBs’ polyimide material withstands higher temperatures than rigid PCBs’ FR4.
Related Reading
Similarities Between Rigid and Flexible PCBs
Rigid PCBs are not completely different from flex PCBs. There are certain similarities between both PCBs as well. A major similarity between flex PCBs and rigid PCBs is the two PCBs perform similar functions. In addition, both PCBs are built in similar ways; nevertheless, flex PCBs make use of flexible circuit coverlay for protection, while rigid PCBs use solder masks for protection.
The manufacturing and designing of rigid PCBs slightly differ from flex PCBs. As a PCB designer or manufacturer, you must be careful when designing either PCB and ensure you follow the requisite design rules. These include minimum space, trace width, minimum hole size, design thickness, and several other factors.
A device can be designed with both PCBs In it. A laptop PC is a common device with both rigid and flex PCBs. Some parts of the laptop require rigid PCB for its functionality while the other parts require flex PCBs for the smooth and correct transfer of information.
Real-World Applications of Rigid PCB and Flex PCB
Rigid PCBs and flex PCBs serve diverse industries, each excelling in specific use cases. Below are their key applications, with examples of JHYPCB’s expertise:
Rigid PCB Applications
- Consumer Electronics: Desktops, TVs, and gaming consoles rely on rigid PCBs for their robust structure. JHYPCB supplied high-performance rigid PCBs for a leading TV brand.
- Industrial Equipment: Rigid PCBs power robotics and control systems due to their mechanical strength. Explore our industrial PCB solutions.
- Networking Devices: Routers and switches use rigid PCBs for complex circuitry and thermal management.
Flex PCB Applications
- Wearable Technology: Smartwatches and fitness trackers use flex PCBs for ergonomic designs. JHYPCB provided lightweight flex PCBs for a smart wristband project.
- Automotive Electronics: Flex PCBs enable complex wiring in infotainment and safety systems. See our automotive PCB services.
- Medical Devices: Pacemakers and surgical tools leverage flex PCBs for compactness, with JHYPCB ensuring reliability.
- Aerospace & Defense: Missiles and satellites use flex PCBs for their lightweight and vibration resistance.
How to Choose Between Rigid PCB and Flex PCB for Your Project
Selecting between rigid PCBs and flex PCBs depends on your project’s specific requirements, such as size, environment, and budget. Understanding the differences between rigid PCB and flex PCB is crucial for making an informed decision. Below, we outline key factors to consider, including a comparison table and practical guidance to help you choose the right PCB type. JHYPCB’s experts are here to assist—contact us for tailored PCB solutions!
Key Factors for Choosing Rigid vs Flex PCB
| Factor | Rigid PCB | Flex PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Size & Form Factor | Ideal for larger, stable devices | Suits compact, flexible designs |
| Environmental Durability | Best for controlled environments | Resists vibrations, heat, shocks |
| Cost | Cost-effective for high-volume | Higher cost, better for prototypes |
| Connectors | Robust, standard connectors | Specialized connectors needed |
| Design Complexity | Supports dense, complex layouts | Enables 3D routing, HDI designs |
- Product Size and Form Factor: Rigid PCBs are perfect for devices with ample space, like desktop computers or industrial controllers. Flex PCBs excel in compact applications, such as smartwatches or foldable smartphones. For example, JHYPCB designed a flex PCB for a compact IoT sensor, saving 30% space.
- Durability and Environmental Conditions: Flex PCBs absorb vibrations and resist heat, making them ideal for automotive or aerospace applications exposed to harsh conditions. Rigid PCBs suit stable, indoor settings like consumer electronics.
- Cost and Production Volume: Rigid PCBs are economical for high-volume production due to simpler manufacturing. Flex PCBs, while costlier, are advantageous for low-volume or prototype runs.
- Connector Requirements: Rigid PCBs support standard connectors for easy assembly, while flex PCBs require specialized connectors for reliable interconnects, common in dynamic applications like laptops.
- Design Complexity: For high-density interconnect (HDI) designs, rigid-flex PCBs combine the strengths of both, ideal for smartphones or medical devices. Explore our rigid-flex PCB services.
Decision Guide
- Choose Rigid PCBs if your project involves stable, high-volume production with complex circuitry, such as networking equipment or industrial machinery.
- Choose Flex PCBs for compact, lightweight, or dynamic applications like wearables or automotive electronics.
- Consider Rigid-Flex PCBs for hybrid needs, balancing stability and flexibility in devices like foldable phones.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rigid and Flex PCBs
Rigid PCBs typically use glass-reinforced epoxy laminate as the core material, with copper layers for circuitry. Other materials like aluminum or ceramics can also be used depending on application requirements.
Flexible PCBs can have up to 8 layers, though most applications use 1-4 layers. The number of layers depends on design complexity and routing needs.
Yes, flexible PCBs generally cost more than rigid PCB boards due to the specialized materials and manufacturing processes involved.
Absolutely. Many products leverage rigid-flex PCB technology which combines rigid and flexible substrates in a single PCB to meet design requirements.
HDI PCBs are used in compact electronics like smartphones, tablets, laptops where complex functionality needs to be packed into a small footprint.
Rigid PCB boards typically have better thermal performance due to their thicker copper layers and ability to integrate heat sinks. Flex PCBs require special thermal management techniques.
A flexible printed circuit board (flex PCB) is made of flexible polymer materials that allow it to be bent, twisted, or folded into various shapes without compromising functionality. Flex PCBs provide versatility in compact electronics.
A rigid PCB is the conventional type of printed circuit board made of inflexible materials like fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin. Rigid PCB boards provide structural rigidity but cannot be bent or folded.
A rigid-flex PCB combines rigid and flexible circuit board materials into one integrated design. The rigid portions provide stiffness, while the flexible layers allow dynamic bending for complex routing.
FPC refers to fully flexible circuit boards made entirely of polymer substrates. Rigid-flex PCBs incorporate both rigid and flexible layers into a single stackup.
FR4 is a rigid, fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate material used for rigid PCBs. Flex PCBs use flexible polymer films like polyimide or polyester as the substrate material.
Key advantages of flex PCBs include compact packaging, lighter weight, improved reliability against vibrations/shocks, and the ability to fit into tight spaces with 3D routing.
Flexible PCBs are typically made using polyimide or polyester substrates with copper circuitry layers and a protective coverlay film.
FR4 is a rigid laminate material, while polyimide is a flexible polymer film. Polyimide offers better heat resistance and dimensional stability suitable for flex PCB fabrication.
FR4 is a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy material, while PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is a fluoropolymer material offering excellent dielectric properties and chemical resistance, though more expensive than FR4.
Rigid PCBs use inflexible materials like FR4, ideal for stable structures like TVs and industrial systems. Flex PCBs use polyimide, allowing bending for wearables and automotive electronics. They differ in flexibility, cost, and durability.
Yes, flex PCBs typically cost more due to specialized materials (e.g., polyimide) and complex manufacturing. However, they can be cost-effective for low-volume prototypes.
Absolutely! Rigid-flex PCBs combine both, offering stability and flexibility, as seen in laptops and medical devices. Explore our rigid-flex PCB services.
Flex PCBs are used in wearables (e.g., smartwatches), automotive infotainment, medical devices (e.g., pacemakers), and aerospace, thanks to their lightweight and vibration resistance.
Consider size, environment, and budget. Flex PCBs suit compact, dynamic applications; rigid PCBs are cost-effective for high-volume, stable designs.
Conclusion
The global PCB market, valued at approximately $81 billion in 2024 according to Statista, is fueled by applications in smartphones, wearables, automotive electronics, and aerospace. The differences between rigid PCB and flex PCB—flexibility, cost, and durability—define their roles in these industries. Flex PCBs shine in innovative foldable devices, while rigid PCBs offer cost-effective solutions for traditional electronics.
JHYPCB provides end-to-end solutions for rigid PCBs, flex PCBs, and rigid-flex designs, ensuring your project’s success. Contact us today for a custom PCB quote!
Recommended Reading
- What is the difference between SMT and SMD?
- What is the difference between wave soldering and reflow soldering?
- What is the difference between Single-Sided PCB and Double-Sided PCB?
- What is the defference between PCB and PCBA?
- The Difference Between Gold Plating and Immersion Gold
- What Are The Advantages And Applications Of Rigid-Flex PCBs?
- What is a PCB Manufacturer? The Definitive Guide
- Custom Flex PCB:Tailored Solutions for Your Applications
- Custom PCB Fabrication in China – Prototyping & Mass Production
- Expedited PCB Services – Quick Turnaround for Your Urgent Needs
- Rapid PCB Prototyping and Production – The Keys to Accelerating Your Product Launch
- Shenzhen – The Global Hub for High-Quality PCB Assembly Manufacturing
- Evaluating and Selecting Quick-Turn PCB Assembly Manufacturers in China