Table of Contents
Introduction to Rigid-Flex PCBs
Are you struggling with bulky PCB designs or unreliable connections in compact devices? Rigid-flex PCBs offer a game-changing solution, combining the durability of rigid circuits with the adaptability of flexible ones. With benefits like up to 50% cost savings, enhanced reliability, and streamlined assembly, rigid-flex PCB designs are transforming industries from medical to aerospace. This guide dives into the key advantages of rigid-flex PCBs, their diverse applications of rigid-flex PCBs, and why they outperform traditional PCBs for modern electronics.

What Are Rigid-Flexible PCB?
Structure of Rigid-Flex PCBs
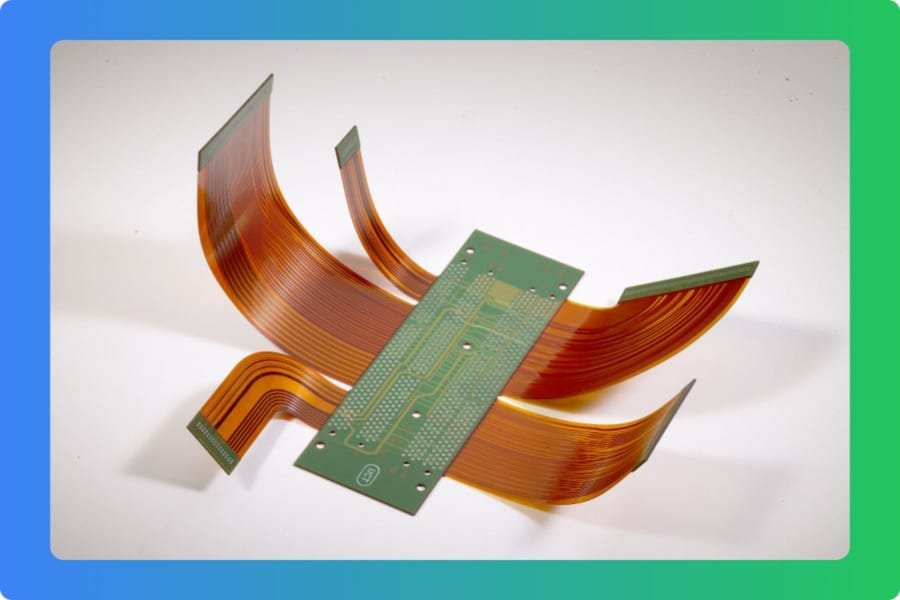
Rigid-flex PCBs combine the strength of rigid circuit boards with the adaptability of flexible circuits, creating a versatile solution for modern electronics. These boards consist of flexible substrate layers, typically made of polyimide, bonded to rigid sections using a pre-preg sheet (a resin-based bonding material). The rigid and flexible areas are connected through plated through-holes, ensuring seamless signal transmission and compact rigid-flex PCB design. This hybrid structure allows devices to maintain durability while fitting into tight or complex spaces.
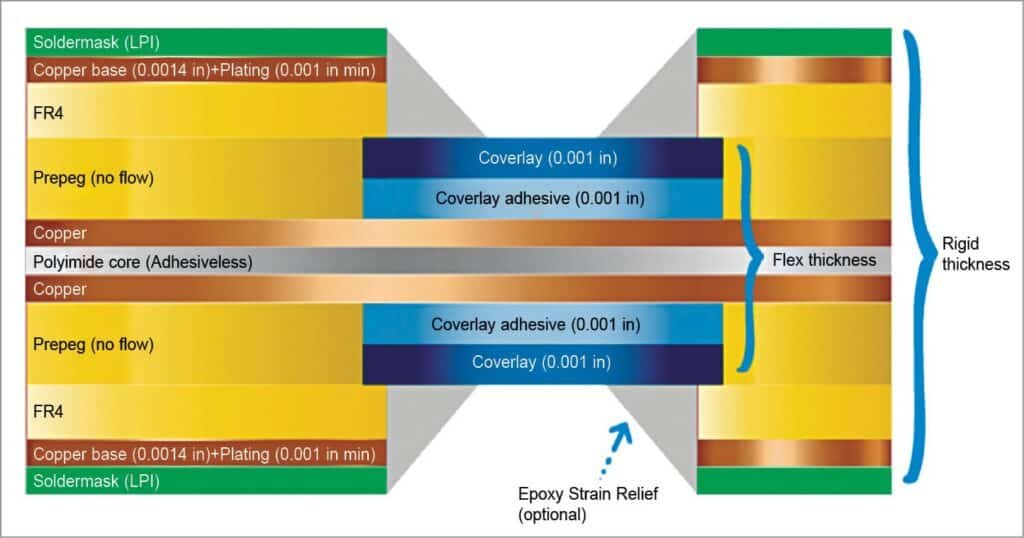
Key Features of Rigid-Flex PCBs
The flexible portion of a rigid-flex PCB is typically single-sided, while the rigid section can support multiple layers for complex circuitry. This design offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced flexibility for dynamic or foldable applications.
- Controlled impedance for consistent high-frequency performance.
- Reduced connection points, eliminating issues like cold joints.
- Lightweight construction, minimizing overall device weight.
- Space savings, freeing up room for additional components.
For example, in a rigid-flex PCB manufacturing process, materials like FR-4 (for rigid sections) and polyimide (for flexible sections) are carefully layered to balance strength and flexibility. Learn more about flex PCB manufacturing to explore material choices and processes.
Advantages of Rigid-Flex PCBs

Flexible Rigid-Flex PCB Design Options
Rigid-flex PCBs enable rigid-flex PCB design flexibility, supporting complex configurations with connectors and components typically found in rigid boards. Flexible sections adapt to tight spaces or corners, while rigid areas provide structural support. For instance, wearable devices often rely on this versatility to fit intricate designs into compact forms.
Reduced Weight and Package Size
By integrating rigid and flexible circuits, rigid-flex PCBs reduce package weight and size by up to 30% compared to traditional PCBs. This streamlined rigid-flex PCB manufacturing process creates sleek, lightweight products like drones or portable medical devices, enhancing portability and efficiency.
High Component Density Applications
Rigid-flex PCBs excel in high-density applications, where space constraints demand compact, high-performance circuitry. Their controlled impedance ensures consistent high-frequency performance, ideal for lightweight conductors in smartphones or aerospace sensors. A 2023 industry report noted a 25% increase in demand for such designs in miniaturized electronics.
Minimal Interconnections and Parts
Unlike traditional PCBs, rigid-flex PCBs require fewer connectors and parts, reducing assembly complexity and boosting productivity. This efficiency can lower production costs by up to 20%, as seen in automotive electronics manufacturing, where fewer connections streamline assembly lines.
Enhanced Connection Reliability
Fewer interconnections in rigid-flex PCBs minimize potential failure points, such as cold joints, improving overall reliability. This durability is critical for mission-critical applications like military communication systems, ensuring consistent performance under demanding conditions.
Lower Assembly Costs
With reduced parts and connections, rigid-flex PCBs cut assembly and procurement costs. A feasibility study during prototyping can further reduce development time by 15%, minimizing supply chain risks and accelerating time-to-market for products like IoT devices.
Resistance to Vibration and Shock
Rigid-flex PCBs withstand harsh conditions, including high temperatures, radiation, and mechanical shock. Their robust design protects heavy components from vibration, making them ideal for aerospace systems or industrial equipment exposed to rugged environments.
Applications of Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs are driving innovation across industries by enabling compact, reliable, and high-performance electronics. Their ability to combine flexibility with durability makes them essential for applications ranging from consumer gadgets to advanced aerospace systems. Below are key applications of rigid-flex PCBs in various sectors.
Rigid-Flex PCBs in Medical Devices
In the medical industry, rigid-flex PCBs power compact devices like pacemakers, cochlear implants, and handheld monitors. Their lightweight and flexible design ensures reliable performance in tight spaces, supporting life-critical applications.
Rigid-Flex PCBs in Military Equipment
Rigid-flex PCBs in military applications enable lightweight, durable systems such as weapon guidance, GPS tracking, and surveillance equipment. Their resistance to shock and vibration ensures performance in harsh environments, critical for mission-critical operations like missile-launch detection.
Rigid-Flex PCBs in Aerospace Systems
In aerospace, rigid-flex PCBs support radar equipment, control tower electronics, and motion sensors. Their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and radiation makes them ideal for space-constrained systems like satellites. According to IPC, rigid-flex adoption in aerospace grew by 15% in 2024.
Rigid-Flex PCBs in Telecommunications
Rigid-flex PCBs in telecommunications power high-frequency systems like 5G base stations, communication satellites, and signal processing units. Their controlled impedance ensures reliable data transmission, supporting the growing demand for faster, more efficient networks.
Rigid-Flex PCBs in Automotive Systems
In the automotive industry, rigid-flex PCBs drive electronic control modules, navigation systems, and infotainment displays. Their compact design and durability enhance vehicle performance, as seen in electric vehicles where space and weight savings are critical.
Rigid-Flex PCBs in Industrial and Manufacturing
Rigid-flex PCBs in industrial applications support test equipment, control panels, and automation systems. Their resistance to vibration and harsh conditions ensures reliability in industrial ACs and CCTV systems, optimizing manufacturing efficiency.
Rigid-Flex PCBs in Consumer Appliances
From TV remotes to smart washing machines, rigid-flex PCBs enable compact, cost-effective consumer electronics. Their flexibility supports innovative designs in solar power controllers and UV water purifiers, meeting the demand for sustainable technology.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rigid-Flex PCBs
What Are Rigid-Flex PCBs Used For?
Rigid-flex PCBs are used in compact, high-reliability applications across industries like medical, aerospace, and automotive. They power devices such as pacemakers, radar systems, and navigation modules, offering flexibility and durability in space-constrained designs.
How Do Rigid-Flex PCBs Differ From Traditional PCBs?
Unlike traditional PCBs, which are either rigid or flexible, rigid-flex PCBs combine both, reducing weight, minimizing connections, and enhancing reliability. This rigid-flex PCB design cuts assembly costs by up to 50% and supports complex, high-density layouts.
What Are the Cost Benefits of Rigid-Flex PCBs?
Rigid-flex PCBs reduce production costs by minimizing parts, connectors, and assembly time. For example, a 2024 industry study reported up to 20% savings in automotive electronics manufacturing due to streamlined rigid-flex PCB manufacturing processes.
Are Rigid-Flex PCBs Suitable for Harsh Environments?
Yes, rigid-flex PCBs are designed to withstand high temperatures, radiation, and mechanical shock, making them ideal for aerospace, military, and industrial applications. Their robust construction ensures performance in demanding conditions.
How Can I Get Started with Rigid-Flex PCBs?
Partner with an experienced manufacturer like JHYPCB to design and prototype rigid-flex PCBs tailored to your needs. Contact us to discuss your project and request a quote today!
Conclusion: Why Choose Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs are a transformative solution, blending the durability of rigid circuits with the adaptability of flexible ones. Their compact design, high reliability, and cost efficiency—saving up to 50% in production costs—make them ideal for industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive. From enabling sleek wearable devices to powering robust 5G telecom systems, rigid-flex PCB applications deliver unparalleled performance.
With over 20 years of expertise, JHYPCB offers high-quality rigid-flex PCB manufacturing, ensuring precision and reliability for your projects. Our team is ready to collaborate on tailored solutions to meet your unique needs. Request a Quote Today and unlock the potential of rigid-flex PCBs for your next innovation!
Related Reading
- Key Process Flow of Rigid-Fled PCB Production
- What factors determine the price of PCB?
- What is Flexible PCB Prototype?
- Development and Applications of FPC Flexible PCB
- 16 Factors Affecting The Cost And Price of Flexible PCB
- What is a Multilayer PCB and What are the Advantages?
- What is a PCB Manufacturer? The Definitive Guide
- Custom Flex PCB:Tailored Solutions for Your Applications
- Custom PCB Fabrication in China – Prototyping & Mass Production
- Rapid PCB Prototyping and Production – The Keys to Accelerating Your Product Launch
- JHYPCB: The Best Prototype PCB Manufacturer for Your Needs
- Applications of Different Types of PCBs in Major Industries
- What Is Flexible PCB Coverlay (FPC Cover Layer)?
- The Manufacturing Process Of Double-sided Flexible PCB Coverlay
- Rigid PCB vs Flex PCB: What Is The Difference?
- The terms you have to know related to the manufacture of Flexible PCB
- Knowledge of Flexible PCB Manufacturing Process Steps