Table of Contents
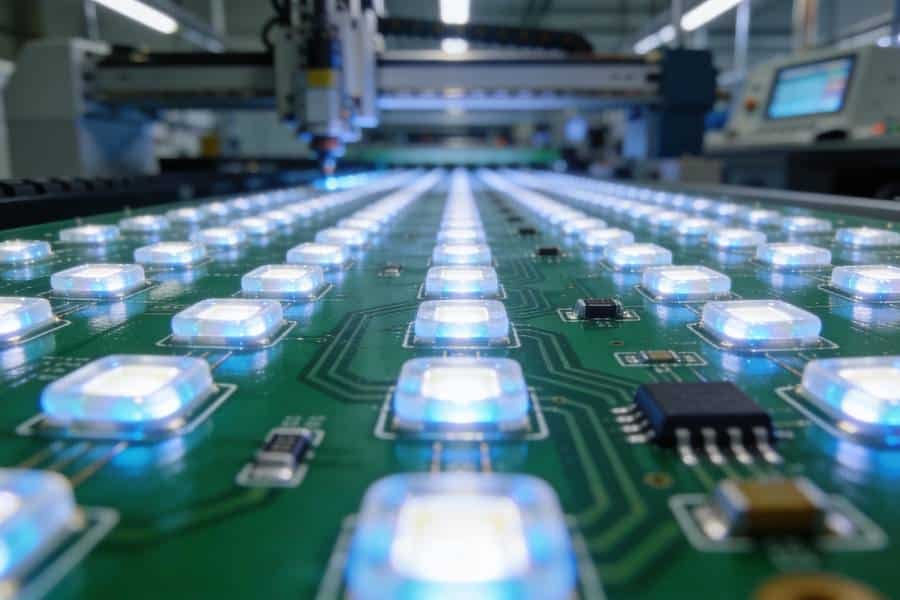
In the fast-evolving world of LED lighting, selecting the right PCB material is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and efficiency. Poor material choices can lead to overheating, reduced lifespan, and diminished light output, while strategic selection enhances thermal management and reliability. Explore our LED PCB Manufacturing & Assembly services for expert support.
Why Material Matters for LED PCBs
LEDs generate significant heat during operation, making thermal dissipation a top priority for high-power applications like streetlights, automotive headlights, and display backlights. Standard FR4 substrates often fall short due to their low thermal conductivity (around 0.3 W/mK), necessitating advanced options like metal-core PCBs (MCPCBs). Proper material strategies can boost LED efficiency by 20-50% and extend operational life beyond 50,000 hours.
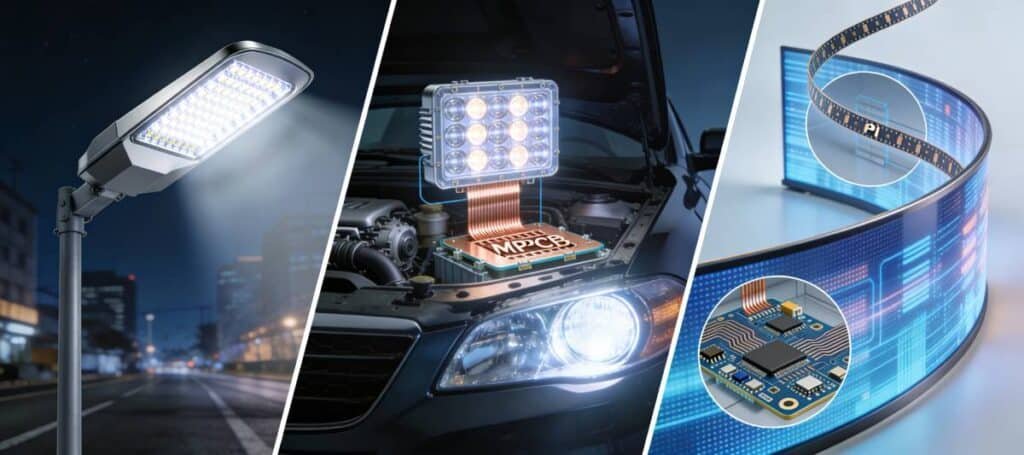

LED PCB Key Requirements
LED PCBs must meet stringent requirements to handle the unique challenges of high-power lighting applications, where heat generation directly impacts performance and reliability. Key demands include excellent thermal conductivity above 1.0 W/mK, mechanical stability to withstand thermal cycling, and compatibility with high operating temperatures exceeding 100°C.
Core Requirements
- Thermal Management: LEDs convert only 20-30% of energy to light, with the rest becoming heat; materials must efficiently transfer heat away from chips to prevent junction temperatures from exceeding 150°C, which halves lifespan per 10°C rise.
- Electrical Insulation: Dielectric layers need high voltage withstand (>2kV) and low CTE mismatch with LEDs (around 17 ppm/°C) to avoid delamination or cracking.
- Mechanical Durability: Substrates should resist warping under solder reflow (260°C) and vibration, especially in automotive or outdoor uses, while maintaining thickness uniformity (1.0-3.0mm).
- Cost-Effectiveness: Balance performance with affordability for mass production, favoring scalable options like aluminum over premium copper.
Standard FR4 (0.3 W/mK conductivity) suffices for low-power indicators but fails in high-lumen LEDs, leading to hotspots and 30-50% efficiency loss.
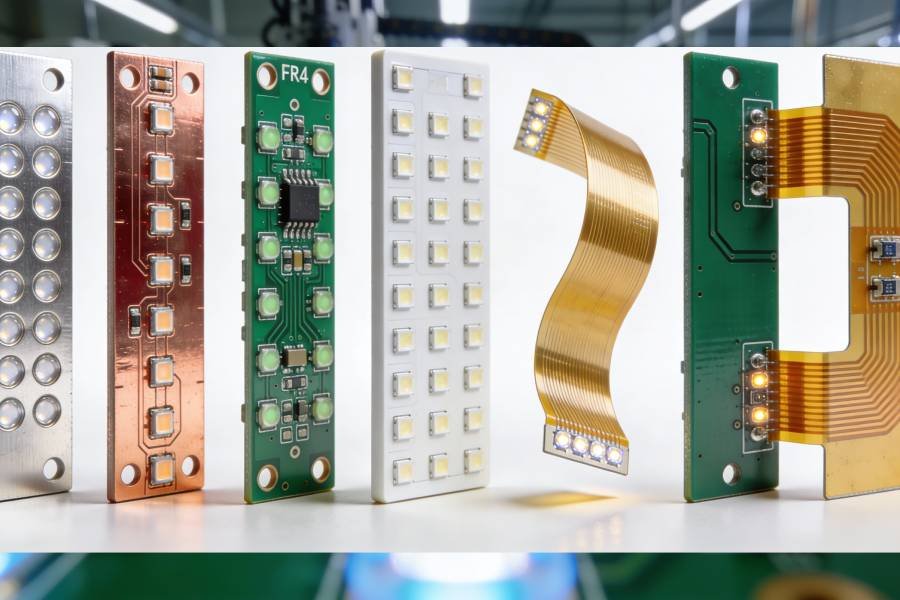
Common PCB Material Types
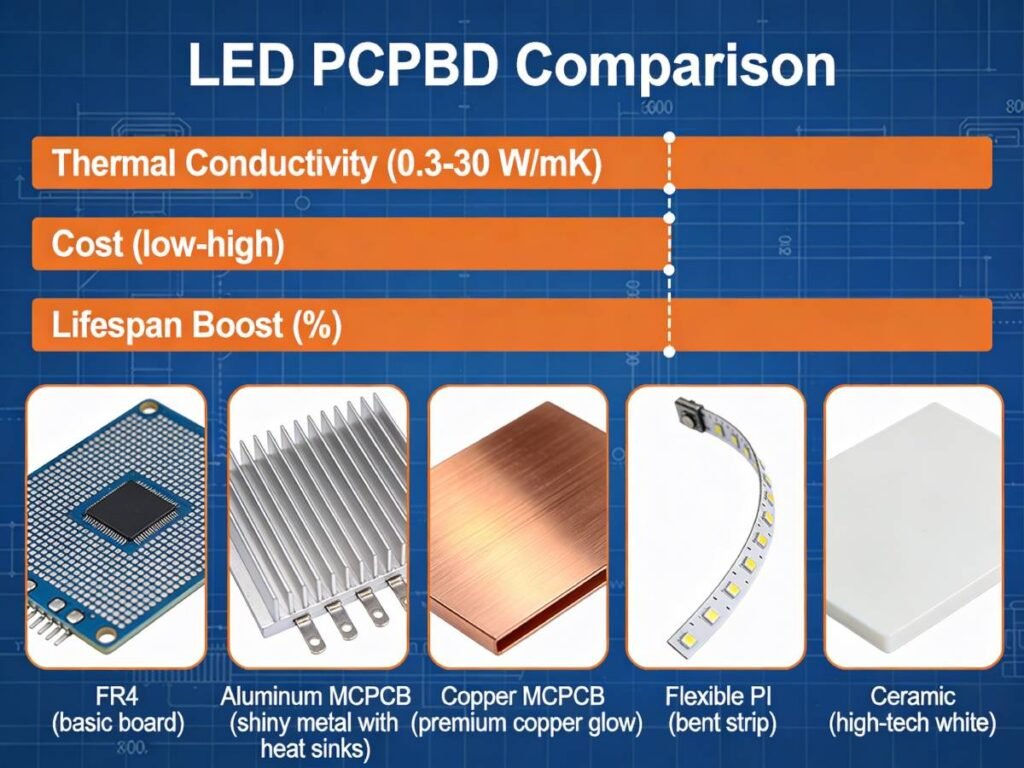
Common PCB materials for LED applications vary in thermal performance, cost, and suitability, with choices driven by power density and design constraints. Aluminum-based MCPCBs dominate due to their balance of heat dissipation and affordability, while others serve niche needs.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) | Key Advantages | Typical LED Use Cases | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR4 | 0.3 | Low cost, easy fabrication | Low-power indicators, displays | Poor heat dissipation, hotspots in >1W LEDs |
| Aluminum MCPCB | 1-2 | Excellent thermal transfer, lightweight | Streetlights, bulbs, strips | Moderate conductivity for ultra-high power |
| Copper MCPCB | 3-8 | Superior heat spreading | High-power floodlights, projectors | Higher cost, heavier |
| Flexible PI (Polyimide) | 0.2-0.4 | Bendable, high Tg (>250°C) | Curved displays, wearables | Lower thermal performance |
| Ceramic | 20-30 | Extreme thermal/electrical isolation | Automotive, aerospace LEDs | Expensive, brittle |
Aluminum MCPCBs, with 1.0-1.6mm cores, offer the best value for most applications, improving LED lifespan by 2-3x over FR4.
Material Selection Strategies
Selecting the right PCB material for LED applications requires a structured strategy that aligns power requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints with material properties. This approach minimizes risks like thermal failure while maximizing performance and cost efficiency.
Key Selection Strategies
- Match Power Density to Material: Use FR4 for <1W LEDs, aluminum MCPCB for 1-10W (e.g., bulbs), and copper or ceramic for >10W high-lumen arrays to ensure junction temperatures stay below 105°C.
- Evaluate Environmental Factors: Opt for corrosion-resistant coatings on aluminum for outdoor/humid use; prioritize high Tg (>170°C) materials for automotive vibration and reflow soldering.
- Balance Thickness and CTE: Select 1.0-1.6mm core thickness for optimal heat spreading without excess weight; aim for CTE near 17 ppm/°C to match silicon LEDs and prevent warpage.
- Perform Cost-Performance Analysis: Prototype with mid-tier aluminum (1-2 W/mK) before scaling; factor in tooling, volume, and lifecycle costs—aluminum often yields 20-30% savings over copper.
Testing via thermal simulation tools like ANSYS validates choices early.
Design and Implementation Best Practices
Implementing effective design and manufacturing practices ensures selected PCB materials perform optimally in LED applications, bridging the gap between theory and reliable production. These best practices focus on layout optimization, thermal enhancements, and collaboration with experienced manufacturers to avoid common pitfalls like hotspots or assembly failures.
Essential Design Tips
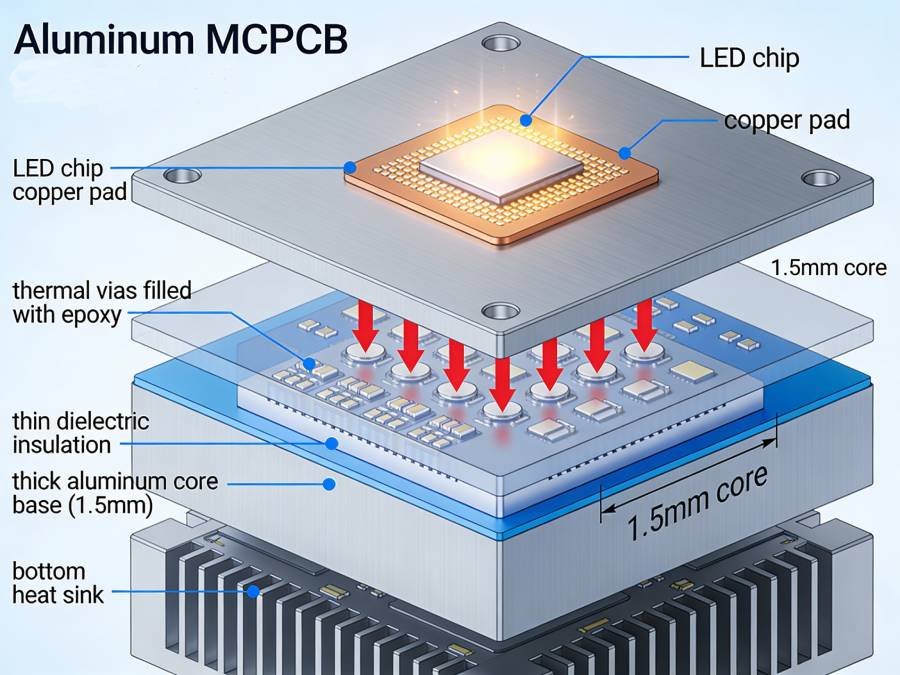
- Thermal Via Arrays: Place 0.3mm vias under LED pads, filled with thermal epoxy, to channel heat from top copper layers to the metal core, improving dissipation by 30-50%.
- Copper Pour and Thickness: Use 2-3 oz copper planes for heat spreading; solid pours around LEDs reduce thermal resistance without adding vias.
- Silkscreen and Solder Mask: Apply white solder mask for reflectivity (boosting light output 5-10%) and thermal vias in mask openings for direct chip bonding.
Manufacturing Best Practices
- Optimize stackup with 1.5mm aluminum core, 1.0mm dielectric (≥1.0 W/mK), and 35µm copper; ensure CTE matching to prevent bow/warp under reflow.
- Conduct thermal profiling and AOI testing during assembly to verify <10°C pad temperature rise.
- Scale from prototypes to volume with DFM reviews for yield >98%.
Conclusion
Choosing the right PCB material elevates LED applications from adequate to exceptional, delivering superior thermal performance, extended lifespans, and enhanced efficiency. By following these strategies—from material matching to design optimization—engineers can reduce failure rates by up to 50% and achieve reliable, high-output lighting solutions. Contact JHYPCB today for a free quote on our LED PCB Manufacturing & Assembly services.