Table of Contents
The lighting industry has undergone a remarkable transformation over the past decade, with LED technology leading the charge toward more efficient, durable, and cost-effective solutions. At the heart of this revolution lies a critical component: the LED PCB (Printed Circuit Board). Whether you’re an engineer exploring LED applications, a product designer evaluating lighting solutions, or simply curious about the technology illuminating your world, understanding LED PCBs is essential. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about LED printed circuit boards, from basic principles to advanced applications.
What is an LED PCB? (Definition and Basics)
An LED PCB, or LED Printed Circuit Board, is a specialized circuit board designed specifically to mount and support Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) while providing electrical connections and efficient heat dissipation. Unlike standard PCBs used in general electronics, LED PCBs are engineered with enhanced thermal management capabilities to handle the significant heat generated by LED components.
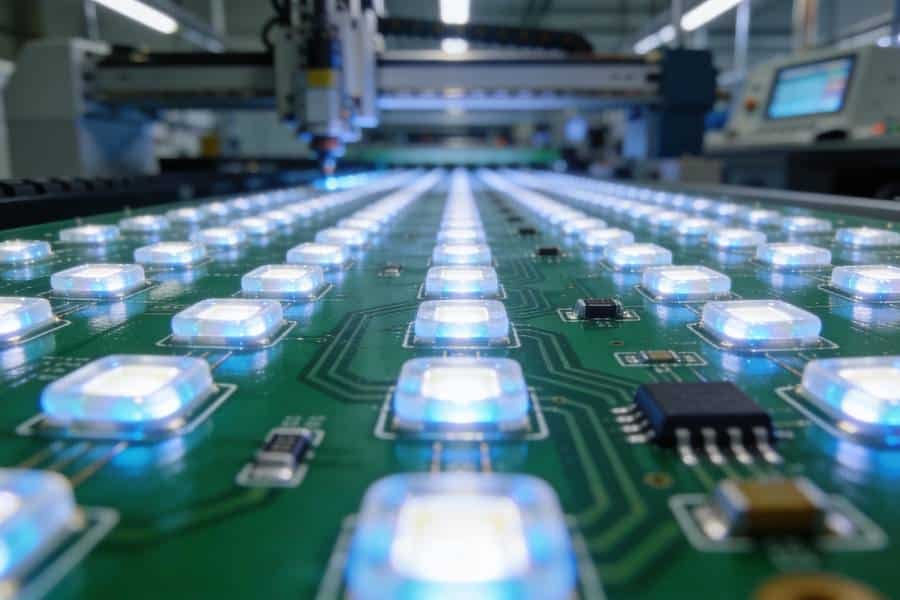
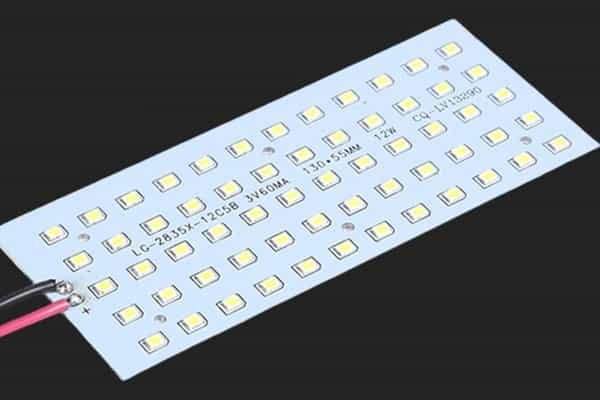
The fundamental purpose of an LED PCB is straightforward: when electrical current flows through the circuit, the LEDs mounted on the board emit light. However, the engineering behind this simple process is sophisticated. Since a single LED is typically not powerful enough to illuminate a large area, multiple LEDs are strategically arranged on the PCB according to specific lighting requirements. This is why you’ll often hear the term “SMD LED PCB board” – SMD (Surface Mount Device) LEDs are compact components that can be densely packed to provide excellent brightness and lumens.
What truly sets LED PCBs apart from conventional circuit boards is their construction. They typically feature a metal core base (often aluminum or copper) that serves as both a structural foundation and a heat sink, ensuring that the LEDs operate within safe temperature ranges and maintain optimal performance over extended periods.
Key Components of an LED PCB
Understanding the anatomy of an LED PCB helps explain why these boards perform so effectively:
- LED Chips/Diodes: These are the light-emitting components themselves, available in various colors, sizes, and power ratings. Modern SMD LEDs are particularly popular due to their compact form factor and high luminous efficiency.
- PCB Substrate: This is the base material that provides structural support. For LED applications, aluminum, copper, or ceramic substrates are commonly used due to their superior thermal conductivity compared to standard FR4 material.
- Thermal Management Layer: Often made of aluminum or copper, this layer acts as a heat spreader, drawing heat away from the LED components and distributing it across a larger area for more effective dissipation.
- Dielectric Layer: This thin, electrically insulating layer sits between the circuit traces and the thermal management layer, preventing electrical shorts while still allowing efficient heat transfer.
- Circuit Traces and Connections: Copper pathways that provide electrical connections between components, power sources, and control circuits.
How Does LED PCB Work?
The working principle of an LED PCB combines electrical engineering and thermal management. When power is supplied to the board, electrical current flows through the circuit traces to the LED components. As current passes through each LED’s semiconductor material, electrons recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons – this is the light you see.
However, not all energy converts to light; a significant portion becomes heat. This is where the LED PCB’s specialized design becomes critical. The heat generated by the LEDs transfers through the dielectric layer to the metal core substrate, which has high thermal conductivity. This substrate then spreads the heat across its surface area, allowing it to dissipate into the surrounding environment or through attached heat sinks.
This efficient thermal pathway is crucial because LED performance and lifespan are highly temperature-dependent. Excessive heat can cause color shift, reduced light output, and premature LED failure. Proper PCB design ensures LEDs operate within their optimal temperature range, maximizing both performance and longevity.
Why LED PCBs Are Important in Modern Lighting
LED PCBs have become indispensable in modern lighting solutions for several compelling reasons:
- Energy Efficiency: LED PCBs convert a higher percentage of electrical energy into light compared to traditional incandescent or fluorescent lighting, resulting in significant energy savings – often 75-80% less power consumption.
- Exceptional Lifespan: One of the most impressive characteristics of LED technology is longevity. A well-designed SMD LED can last up to 100,000 hours on average, and in some cases even more. This translates to approximately 11 years of continuous operation or over 20 years at typical usage rates, far exceeding traditional lighting methods.
- Compact Design: The small form factor of LED components allows for creative and space-efficient lighting designs that were impossible with previous technologies.
- Superior Heat Management: Unlike older lighting methods that struggle with heat dissipation, LED PCBs are engineered specifically to handle thermal challenges, ensuring consistent performance and reliability.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial investment may be higher, the combination of energy savings, reduced maintenance, and extended lifespan makes LED PCBs highly cost-effective over their operational lifetime.
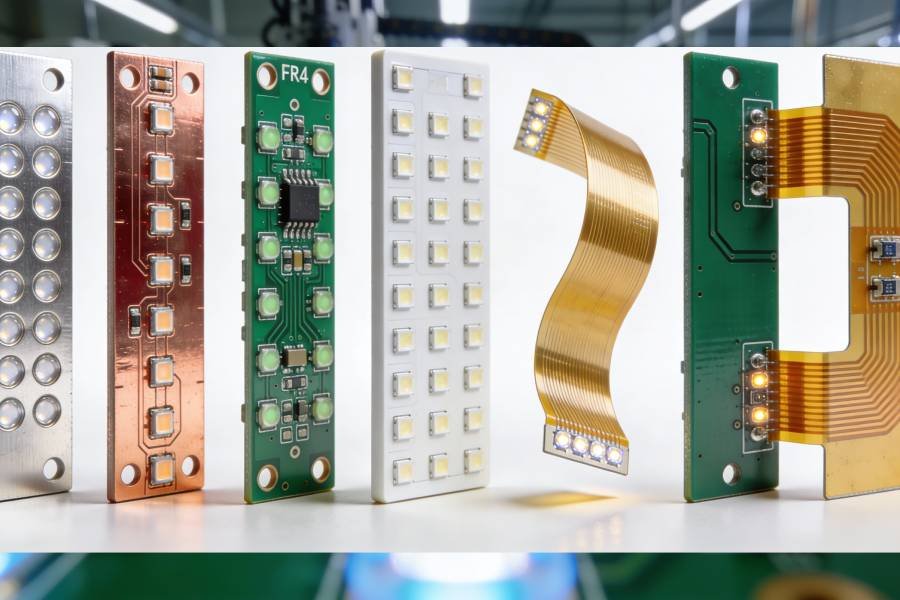
Types of LED PCB Boards (Overview)
LED PCBs come in various types, each optimized for specific applications and performance requirements:
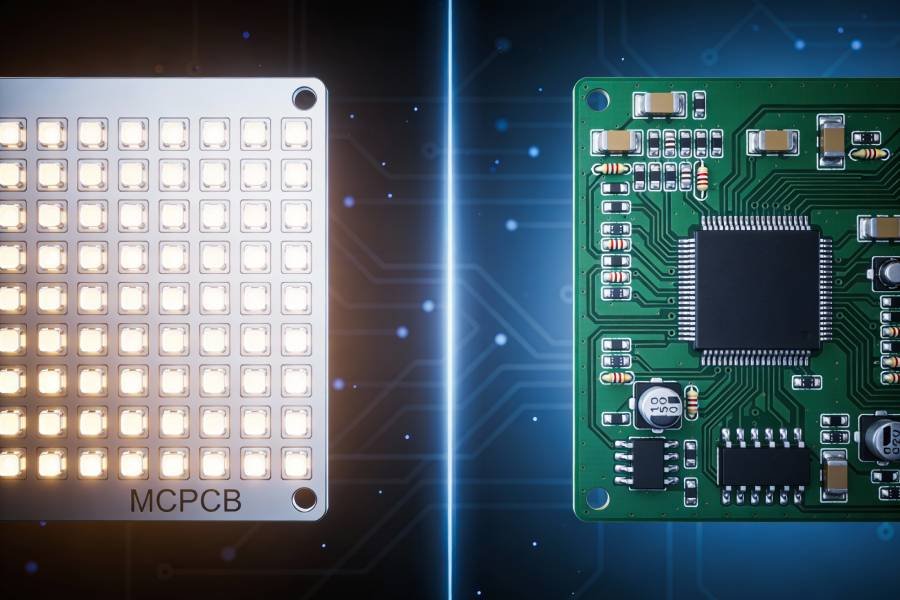
- Aluminum LED PCB (MCPCB): The most widely used type, Metal Core PCBs with aluminum substrate offer an excellent balance of thermal performance and cost-effectiveness. They’re ideal for general lighting applications where good heat dissipation is required without premium pricing.
- Copper Core LED PCB: When aluminum isn’t sufficient, copper core PCBs provide the highest thermal conductivity among mainstream PCB materials. They’re used in high-power LED applications where maximum heat dissipation is critical, though they come at a higher cost.
- FR4 LED PCB: Standard FR4 material is suitable for low-power LED applications where heat generation is minimal. While not optimized for thermal management, FR4 boards are the most economical choice for applications like indicator lights or low-intensity displays.
- Ceramic LED PCB: Offering both high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical insulation, ceramic substrates are ideal for specialized or high-reliability LED applications, particularly in harsh environments or where long-term stability is paramount.
- Flexible LED PCB: Using polyimide or polyester substrates, flexible LED PCBs can bend and conform to curved surfaces, making them perfect for wearable technology, automotive interior lighting, and decorative applications where rigid boards won’t work.
- Hybrid LED PCB: Combining different substrate materials in a single board, hybrid PCBs leverage the benefits of multiple technologies to meet specific performance requirements.
For a detailed comparison of these types and guidance on which is best for your application, check out our comprehensive article on 6 Types of LED PCB Boards.
LED PCB vs Standard PCB: What's the Difference?
| Feature | LED PCB | Standard PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Aluminum, copper, or ceramic for thermal conductivity | FR4 fiberglass composite |
| Thermal Conductivity | 1-8 W/mK (much higher) | 0.3-0.4 W/mK |
| Typical Thickness | 1.0-3.0mm (thicker for heat dissipation) | 0.4-1.6mm |
| Primary Purpose | LED mounting with thermal management | General electronic circuits |
| Heat Dissipation | Engineered specifically for high heat | Limited heat dissipation capability |
| Applications | Lighting systems, displays, indicators | Computers, consumer electronics, industrial controls |
| Cost | Generally higher due to specialized materials | Lower for standard materials |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Requires thermal design considerations | Standard fabrication processes |
The key difference lies in thermal engineering. While standard PCBs can accommodate LEDs, they lack the thermal management infrastructure necessary for reliable, long-term operation in demanding lighting applications.
Common Applications of LED PCB
LED PCBs have penetrated virtually every industry where lighting plays a role:
- Automotive Lighting: From headlights and taillights to interior ambient lighting, automotive applications demand LED PCBs that can withstand extreme temperatures, vibration, and moisture while maintaining consistent performance. The combination of durability, efficiency, and compact size makes aluminum LED PCBs ideal for indicators, brake lights, and dashboard illumination.
- Commercial Lighting: Office buildings, retail stores, and street lighting increasingly rely on LED PCB technology for energy-efficient illumination. These applications benefit from the long lifespan and low maintenance requirements, significantly reducing operational costs over time.
- Consumer Electronics: LED PCBs provide backlighting for televisions, computer monitors, smartphone displays, and tablet screens. The ability to produce thin, uniform light distribution makes them essential for modern display technology.
- Medical Devices: Surgical lighting, diagnostic instruments, and medical displays utilize LED PCBs for their precise, controllable illumination and reliability. The compact size and ability to maintain consistent color temperature are crucial in medical applications.
- Industrial Lighting: Factories, warehouses, and manufacturing facilities use high-power LED PCBs to provide bright, energy-efficient lighting in challenging environments. The durability and heat resistance of metal core PCBs make them well-suited for industrial conditions.
- Architectural Lighting: Designers leverage LED PCBs to create stunning lighting effects for building facades, monuments, landscapes, and interior spaces. The flexibility in design and precise color control enables creative illumination solutions that were previously impossible.
Advantages of Using LED PCB Technology
The widespread adoption of LED PCBs stems from their numerous advantages:
- Superior Heat Dissipation: The engineered thermal pathways in LED PCBs efficiently remove heat from LED components, preventing performance degradation and extending operational life.
- Longer Lifespan and Reliability: With proper thermal management, LED PCBs offer exceptional longevity, reducing replacement frequency and maintenance costs. The solid-state nature of LEDs also makes them more resistant to shock and vibration compared to traditional lighting.
- Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings: LED technology delivers more lumens per watt than any other lighting technology, translating directly to lower energy bills and reduced carbon footprint.
- Compact and Lightweight Design: The small size of LED components and PCBs allows for slim, lightweight lighting fixtures that can fit in spaces where traditional lighting cannot.
- Environmental Benefits: LEDs contain no mercury or other hazardous materials, and the long lifespan means fewer discarded units. Additionally, the materials in LED PCBs are often recyclable.
- Design Flexibility: LED PCBs can be manufactured in various shapes, sizes, and configurations, enabling innovative lighting designs tailored to specific applications.
- Better Light Quality and Control: LED PCBs offer superior color rendering, instant on/off capability, and easy integration with dimming and color-changing systems.
Key Considerations When Choosing LED PCB
Selecting the right LED PCB for your application requires careful evaluation of several factors:
- Power Requirements: Determine whether your application involves low-power indicator LEDs or high-power illumination. High-power applications require substrates with superior thermal conductivity, such as aluminum or copper core PCBs.
- Thermal Management Needs: Assess the operating environment and heat dissipation requirements. Applications in enclosed spaces or high ambient temperatures demand more robust thermal solutions.
- Application Environment: Consider factors like temperature extremes, humidity, vibration, and potential exposure to chemicals or contaminants. Harsh environments may require ceramic or specially coated PCBs.
- Budget Constraints: While aluminum MCPCBs offer excellent performance at reasonable cost, copper core and ceramic options provide superior characteristics at premium prices. FR4 remains the most economical for low-power applications.
- Size and Form Factor: Space constraints may dictate PCB dimensions and shape. Flexible PCBs offer solutions where rigid boards cannot fit or where conforming to curved surfaces is necessary.
- Certification Requirements: Many applications require compliance with safety standards like UL, CE, or RoHS. Ensure your LED PCB manufacturer can provide certified products meeting your regulatory requirements.
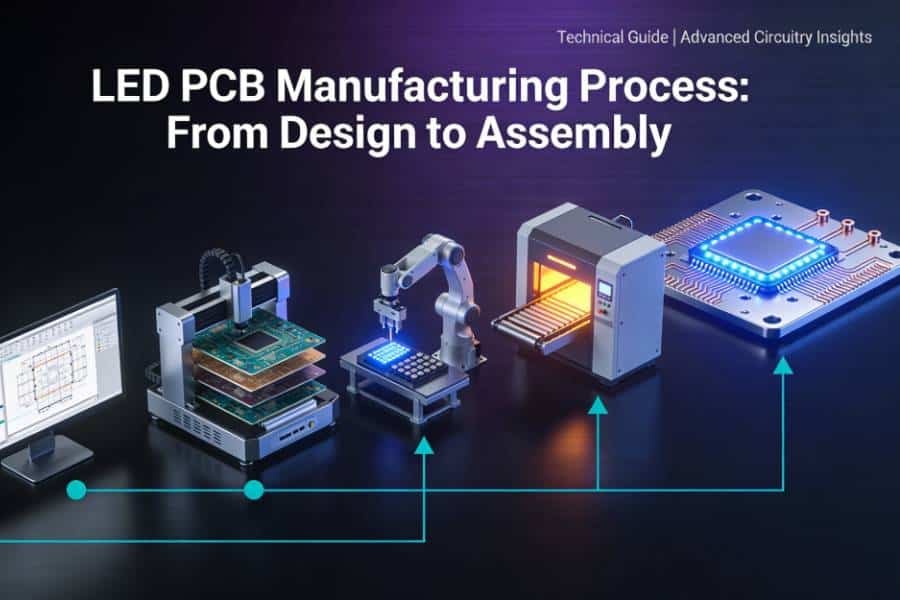
LED PCB Manufacturing Process (Brief Overview)
The journey from concept to finished LED PCB involves several critical stages:
- Design Phase: Engineers create detailed schematics and layouts using specialized PCB design software, considering electrical requirements, thermal management, component placement, and manufacturing constraints.
- Material Selection: Based on application requirements, appropriate substrate materials, copper thickness, and surface finishes are specified.
- PCB Fabrication: The bare PCB is manufactured through processes including imaging, etching, drilling, and surface finishing. For metal core PCBs, this includes bonding the dielectric layer to the aluminum or copper base.
- LED Assembly: Components are mounted onto the PCB using either SMT (Surface Mount Technology) for surface-mount LEDs or through-hole soldering for through-hole components. Many manufacturers use automated pick-and-place machines for precision and efficiency.
- Testing and Quality Control: Completed boards undergo rigorous inspection using Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), X-ray examination, and functional testing to ensure quality and performance standards are met.
For those interested in the detailed manufacturing workflow and quality control measures, our LED PCB Manufacturing Process article provides an in-depth exploration of each stage.
Learn more our LED PCB manufacturing capabilities.
Understanding SMD LED PCB
SMD (Surface Mount Device) LEDs have become the dominant technology in LED PCB applications, and understanding why helps explain the prevalence of “SMD LED PCB board” terminology.
- What is SMD LED?: SMD LEDs are compact light-emitting diodes designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of PCBs using surface-mount technology, eliminating the need for component leads extending through the board.
- Why SMD LEDs Are Widely Used: Their small size allows for higher component density, enabling brighter lighting in smaller spaces. They’re also easier to automate during manufacturing, reducing production costs and improving consistency.
- Benefits: SMD LEDs provide excellent brightness and lumens relative to their size, superior heat dissipation due to direct thermal contact with the PCB, and design flexibility that enables creative lighting solutions.
- SMD LED PCB Board Applications: You’ll find SMD LED PCBs in virtually every modern lighting application, from smartphone camera flash units to large-format video displays and everything in between.
The long lifespan advantage mentioned earlier – up to 100,000 hours – is particularly true of SMD LED implementations on properly designed PCBs with adequate thermal management.
Thermal Management in LED PCB
Thermal management deserves special attention as it’s the single most critical factor in LED PCB performance and longevity.
- Why Heat Management is Critical: LED performance degrades significantly at elevated temperatures. For every 10°C increase in junction temperature, LED lifespan can be cut in half, while light output decreases and color shift occurs.
- Consequences of Overheating: Inadequate thermal design leads to premature LED failure, inconsistent color temperature, reduced light output, and potentially catastrophic failures where LEDs or other components are damaged.
- Basic Thermal Design Principles: Effective LED PCB thermal management involves selecting appropriate substrate materials with high thermal conductivity, using adequate copper thickness for heat spreading, designing thermal vias to conduct heat through the board layers, and ensuring proper heat sink attachment when necessary.
- Thermal Vias and Copper Thickness: Strategic placement of thermal vias under LED components creates thermal pathways through the PCB, while thicker copper layers (2oz or more) improve lateral heat spreading across the board surface.
For applications pushing the limits of LED power density, our detailed guide on Thermal Management in LED PCB explores advanced techniques including thermal simulation, heat sink design, and thermal interface materials.
How to Choose the Right LED PCB Manufacturer
The quality of your LED PCB depends heavily on your manufacturing partner. Here’s what to look for:
- Quality Certifications: Reputable manufacturers should hold certifications like ISO 9001 for quality management, UL or CE for safety compliance, and RoHS for environmental standards. These certifications demonstrate commitment to consistent quality and regulatory compliance.
- Manufacturing Capabilities: Assess whether the manufacturer has experience with the specific type of LED PCB you need. Can they handle metal core PCBs? Do they offer flexible PCB options? What are their minimum and maximum size capabilities?
- Design Support Services: The best manufacturers offer Design for Manufacturing (DFM) feedback, helping you optimize your design for production efficiency and reliability. This collaboration can save significant time and cost while improving final product quality.
- Testing and Quality Control Standards: Inquire about inspection processes. Professional manufacturers employ AOI (Automated Optical Inspection), X-ray inspection for hidden defects, and comprehensive functional testing to ensure every board meets specifications.
- Delivery and Reliability: Consistent on-time delivery, clear communication
Click here to learn why choose JHYPCB for your LED PCB manufacturing.