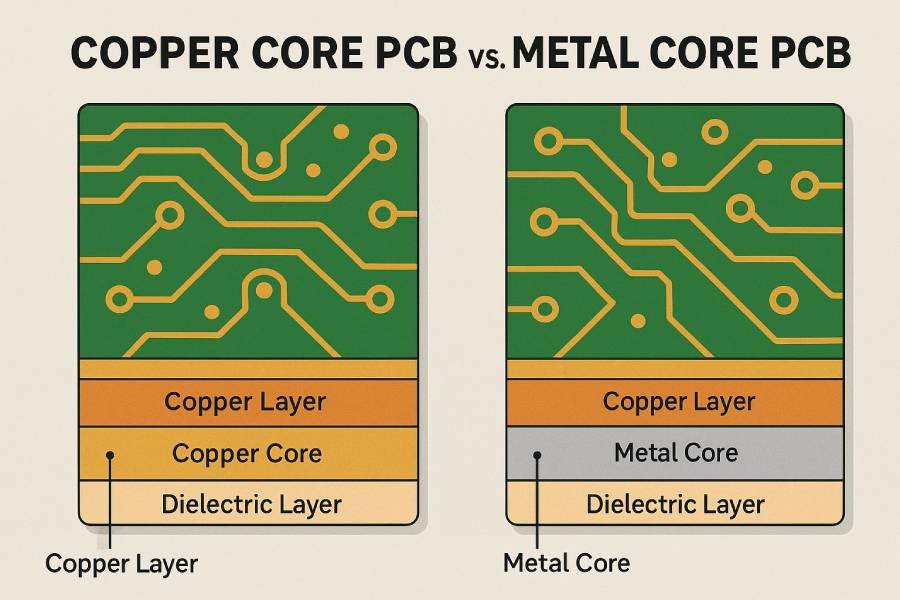
Table of Contents
Introduction
Ever wondered what powers your smartphone, laptop, or even your car’s navigation system? The answer lies in Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), the unsung heroes of modern electronics. These compact yet powerful components are the backbone of countless devices, ensuring they function smoothly and efficiently. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what a PCB in electronics is, how circuit boards work, their types, and their critical role in shaping today’s technology. Whether you’re a curious beginner or an industry professional, JHYPCB, a leading PCB manufacturer in China, is here to provide expert insights and top-tier PCB solutions.
What is a PCB in Electronics?
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a flat, insulating board that connects electronic components using conductive pathways, or traces, etched onto its surface. These traces act like a roadmap, directing electrical signals and power between components such as resistors, capacitors, and microchips to ensure a device operates as intended. Think of a PCB as the nervous system of an electronic device, coordinating communication between its parts to deliver seamless functionality.
PCBs are found in virtually every electronic device, from consumer gadgets like smartphones and TVs to advanced systems in medical equipment and aerospace technology. By providing a reliable platform for component integration, PCBs enable the miniaturization and efficiency that define modern electronics.
For a deeper dive into the manufacturing process of bare circuit boards, check out our detailed guide on What is a Blank PCB?.
Key Features of a PCB
- Compact Design: PCBs allow complex circuits to fit into small spaces, enabling sleek, portable devices.
- Reliability: Precision-engineered traces ensure consistent performance and minimal signal interference.
- Customizability: PCBs can be tailored to meet specific device requirements, from simple to highly complex designs.

How Do Circuit Boards Work?
Understanding how circuit boards work is key to appreciating their role in electronics. At its core, a PCB provides a structured platform for electrical connectivity. Here’s a simplified explanation:
- Conductive Pathways: Copper traces on the PCB connect components, allowing electrical signals and power to flow between them. These traces are carefully designed to match the circuit’s requirements.
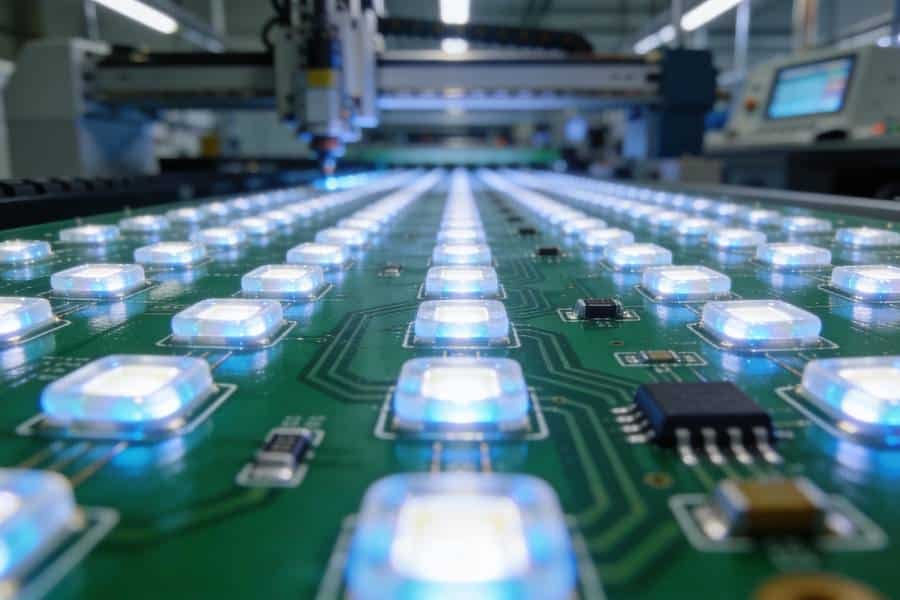
- Component Integration: Components like integrated circuits (ICs), resistors, and capacitors are mounted onto the PCB, either through surface-mount technology (SMT) or through-hole technology (THT).
- Signal Transmission: The PCB ensures signals are transmitted accurately, minimizing interference and maintaining performance.
- Power Distribution: PCBs distribute power efficiently to components, ensuring the device operates reliably.
For example, in a smartphone, the PCB connects the processor, memory, and sensors, enabling the device to process data, display images, and respond to user inputs. This seamless coordination is what makes modern electronics so powerful and versatile.
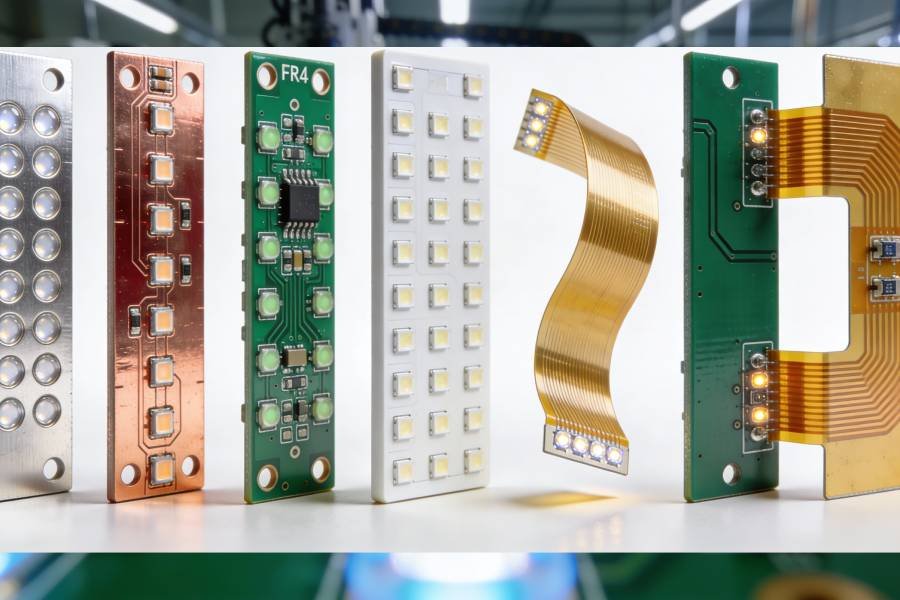
Types of PCBs in Electronics
PCBs come in various types, each designed to meet specific needs based on complexity, flexibility, and application. Here are the most common types:
- Single-Sided PCBs
- Feature a single layer of conductive material on one side of the board.
- Ideal for simple electronics like calculators or basic sensors.
- Cost-effective and easy to manufacture.
- Have conductive layers on both sides, connected via holes called vias.
- Suitable for moderately complex devices like power supplies or LED lighting systems.
- Multilayer PCBs
- Contain multiple layers of conductive material, stacked and insulated for high-density circuits.
- Used in advanced electronics like smartphones, computers, and medical devices.
- Rigid PCBs
- Made from solid materials like FR-4, providing structural stability.
- Common in devices requiring durability, such as laptops and industrial equipment.
- Flexible PCBs
- Use flexible materials like polyimide, allowing the board to bend or fold.
- Ideal for compact or wearable devices like smartwatches.
- Rigid-Flex PCBs
- Combine rigid and flexible sections for enhanced versatility.
- Used in applications like aerospace and medical implants, where both stability and flexibility are needed.
- High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs
- Feature finer traces and smaller vias for compact, high-performance designs.
- Common in advanced consumer electronics and IoT devices.
To learn more about the bare boards used as the foundation for these PCB types, explore our guide on What is a Blank PCB?.

Applications of PCBs in Modern Electronics
PCBs are integral to a wide range of industries, powering devices that shape our daily lives. Here are some key applications:
- Consumer Electronics
- PCBs are found in smartphones, tablets, TVs, and gaming consoles, enabling compact designs and high performance.
- Example: A smartphone’s PCB integrates the processor, camera, and display for seamless operation.
- Automotive Electronics
- Modern vehicles rely on PCBs for navigation systems, engine controls, and safety features like airbags.
- Example: PCBs in electric vehicles manage battery systems and power distribution.
- Medical Devices
- PCBs power life-critical equipment like pacemakers, MRI machines, and diagnostic tools.
- Example: A wearable health monitor uses a flexible PCB to track vital signs comfortably.
- Industrial Electronics
- PCBs support automation systems, robotics, and power management in factories.
- Example: PCBs in industrial sensors ensure precise monitoring of machinery performance.
- Aerospace and Defense
- PCBs in avionics and navigation systems withstand extreme conditions for reliable performance.
- Example: A satellite’s PCB ensures accurate data transmission in harsh environments.
- IoT and Wearables
- PCBs enable compact, connected devices like smart home systems and fitness trackers.
- Example: A smart thermostat uses an HDI PCB for efficient connectivity and control.
These applications highlight the versatility of PCBs, making them indispensable in modern technology. At JHYPCB, we provide customized PCB solutions to meet the unique needs of each industry.

Why Choose JHYPCB for Your PCB Needs?
At JHYPCB, we understand the critical role PCBs play in electronics. With over 15 years of experience, we offer end-to-end PCB manufacturing and assembly services, ensuring high quality and reliability. Our services include:
- PCB Manufacturing: From single-sided to multilayer, rigid, flexible, and rigid-flex PCBs, we deliver precision-engineered boards tailored to your needs.
- PCB Assembly: Our SMT, THT, and turnkey assembly services ensure seamless component integration.
- Component Sourcing: We source high-quality components to streamline your production process.
- SMT Stencil and Prototyping: We provide fast-turnaround prototyping and precision stencils for efficient assembly.
Our state-of-the-art facilities in China and ISO-certified processes guarantee consistent quality, whether you need prototypes or high-volume production. Ready to bring your electronics to life? Contact us at sales@pcbjhy.com for a quote or to discuss your project!
Conclusion
Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the heart of modern electronics, enabling everything from smartphones to life-saving medical devices. By understanding what a PCB in electronics is, how it works, and its diverse applications, you can appreciate its role in shaping technology. Whether you’re designing a new product or exploring PCB solutions, JHYPCB is your trusted partner for high-quality PCB manufacturing and assembly. Reach out to us at sales@pcbjhy.com to start your next project and power the future of electronics!